What Is Anatomical Waste?
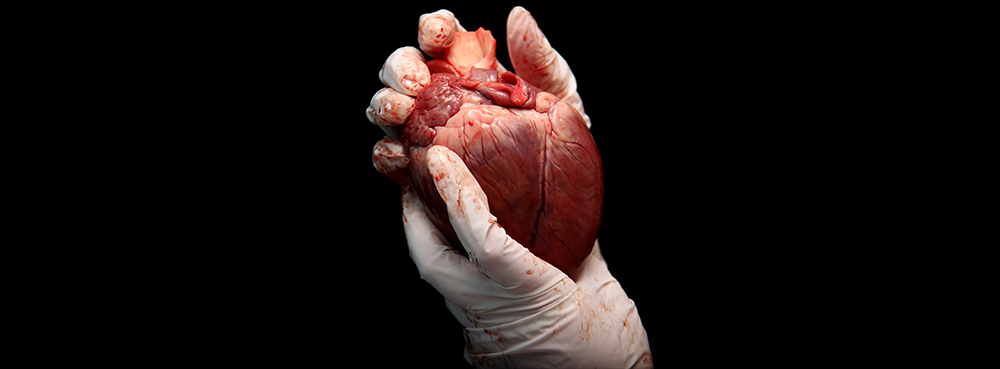
Anatomical waste, or as you may more readily recognise it – body parts, organs and tissues – is a subject that can be uncomfortable to discuss, but crucial to understand if you’re working within healthcare.
It’s a critical concern in healthcare settings, requiring careful management to ensure public safety and environmental protection. This comprehensive guide explores the definition, types, and proper handling of anatomical waste, with a focus on UK regulations and best practices.
TOPICS WE WILL COVER:
1 / Understanding Anatomical Waste
3 / Is Anatomical Waste Hazardous?
4 / Anatomical Waste Colour Coding
5 / Anatomical Waste Management
6 / Challenges in Anatomical Waste Management
7 / Best Practices for Anatomical Waste Management
8 / Sharpsmart’s Anatomical Waste Disposal Services
9 / Future Trends in Anatomical Waste Management
10 / Anatomical Waste Management: Final Thoughts
11 / Partner with Sharpsmart for Safe, Compliant Services Today
Understanding Anatomical Waste
Anatomical waste refers to any waste that consists of human or animal tissue, organs, body parts, or bodily fluids. According to the UK Environment Agency, anatomical waste is a subset of clinical waste and includes:
- Body parts and organs
- Blood bags and blood preserves
- Tissue samples from biopsies or surgical procedures
- Placentas and other birth-related tissues
It’s important to note that anatomical waste is distinct from other types of clinical waste due to its recognisable human or animal origin and the specific disposal requirements it entails.
Anatomical Waste Examples
Common examples of anatomical waste include:
- Surgical specimens (e.g., removed tumours, amputated limbs)
- Biopsy samples
- Placentas and umbilical cords
- Blood, blood products and other body fluids
- Human tissue samples from autopsies or post-mortem examinations
- Animal carcasses or body parts from research facilities
- Extracted teeth* (excluding those with amalgam fillings)
These examples illustrate the diverse nature of anatomical waste and underscore the importance of proper management across various healthcare and research settings.
*Extracted teeth are anatomical waste but a dentist may treat them as non-anatomical infectious waste and dispose of teeth without amalgam in the yellow-lidded sharps receptacle.
Is Anatomical Waste Hazardous?
The classification of anatomical waste as hazardous depends on several factors. According to the Hazardous Waste Regulations 2005, anatomical waste is generally considered hazardous due to its potential to be infectious. However, the specific classification can vary:
- Infectious anatomical waste: This is classified as hazardous waste and requires special handling and disposal.
- Non-infectious anatomical waste: In rare cases where there is sufficient evidence that the waste is non-infectious, it may be classified as non-hazardous. However, this determination must be based on definite knowledge of the waste’s origin and the patient’s medical history.
It’s crucial to note that even non-infectious anatomical waste requires careful handling and disposal due to its sensitive nature and potential psychological impact.
Anatomical Waste Colour Coding 
In the UK, a colour-coding system is used to ensure proper segregation and disposal of different types of clinical waste. For anatomical waste, the designated colour is red.
Anatomical waste containers or bags should have red lids or be entirely red. For a more comprehensive guide to colour-coded medical waste segregation in the UK, check out our article explaining which waste goes into which bin.
Anatomical Waste Management
- Effective anatomical waste management is crucial for maintaining safety and compliance in healthcare settings. The process involves several key steps:
- Segregation: Anatomical waste must be separated from other types of clinical waste at the point of generation.
- Containment: Use leak-proof, rigid containers with red lids specifically designed for anatomical waste.
- Labelling: Clearly label containers with the type of waste and any relevant hazard information.
- Storage: Store anatomical waste in a secure, temperature-controlled area. If storage exceeds 24 hours, refrigeration is typically required.
- Collection and Transport: Only licensed waste carriers should collect and transport anatomical waste.
- Treatment and Disposal: Anatomical waste must be disposed of by incineration at approved facilities.
- Documentation: Maintain accurate records of waste generation, collection, and disposal, including consignment notes for hazardous waste.
Healthcare facilities must comply with the Environmental Protection Act 1990 and the Controlled Waste Regulations 2012 when managing anatomical waste.
Challenges in Anatomical Waste Management
Managing anatomical waste presents several challenges:
- Ethical considerations: The sensitive nature of anatomical waste requires respectful handling and disposal.
- Infection control: Proper management is crucial to prevent the spread of infections.
- Regulatory compliance: Staying up-to-date with evolving regulations can be complex.
- Cost management: Specialised containment, transport, and disposal can be expensive.
- Staff training: Ensuring all personnel are educated on proper handling procedures is ongoing.
- Environmental impact: Balancing the need for safe disposal with sustainability goals.
Best Practices for Anatomical Waste Management
- To address these challenges and ensure safe, compliant anatomical waste management:
- Develop comprehensive policies: Create clear guidelines for handling anatomical waste, aligned with current regulations.
- Provide regular training: Ensure all staff understand correct segregation, containment, and handling procedures.
- Use appropriate containers: Invest in high-quality, leak-proof containers designed specifically for anatomical waste.
- Implement strict segregation: Enforce proper waste segregation at the point of generation to prevent contamination.
- Maintain accurate records: Keep detailed documentation of all anatomical waste from generation to final disposal.
- Partner with reputable waste management providers: Work with experienced, licensed companies specialising in anatomical waste disposal.
- Conduct regular audits: Regularly review and assess your anatomical waste management processes to identify areas for improvement.
Sharpsmart’s Anatomical Waste Disposal Services
Sharpsmart UK offers comprehensive and compliant solutions for anatomical waste disposal. With over 30 years of experience, Sharpsmart has revolutionised healthcare waste management through innovative technologies and a commitment to safety and sustainability. Sharpsmart’s safe management services include:
- Customised waste segregation systems
- Secure, leak-proof containers specifically designed for anatomical waste
- Compliant anatomical waste collection and transportation services
- Safe and environmentally responsible disposal through approved incineration facilities
- Detailed tracking and reporting for regulatory compliance
- Staff training and education programmes
By partnering with Sharpsmart, healthcare facilities can ensure their anatomical waste is managed safely, efficiently, and in full compliance with UK regulations. Sharpsmart’s expertise in navigating complex regulatory requirements and our commitment to sustainability makes us an excellent choice for any healthcare facility looking to improve their anatomical waste management practices.
Future Trends in Anatomical Waste Management
- As healthcare continues to evolve, so too will the approaches to managing anatomical waste. Some emerging trends include:
- Advanced tracking technologies: Implementation of RFID and blockchain for improved waste tracking and accountability.
- Sustainable disposal methods: Research into more environmentally friendly alternatives to incineration.
- Automated segregation systems: Development of AI-powered systems to improve waste segregation accuracy.
- Enhanced staff training: Use of virtual and augmented reality for more effective training programmes.
- Stricter regulations: Potential for more stringent guidelines on anatomical waste management and disposal.
Anatomical Waste Management: Final Thoughts
Effective management of anatomical waste is crucial for protecting public health, ensuring worker safety, and maintaining environmental integrity.
By understanding what constitutes anatomical waste, following proper disposal procedures, and adopting innovative solutions, healthcare facilities can significantly reduce the risks associated with this sensitive waste stream.
As the healthcare sector continues to grow and evolve, so too will the strategies for managing anatomical waste, driving towards a safer and more sustainable future.
Partner With Sharpsmart For Safe, Compliant Services Today
Partnering with experienced providers like Sharpsmart UK ensures that anatomical waste is handled safely, sustainably, and in compliance with all relevant regulations.
Contact us today for a free consultation and empower your facility with industry-leading service in the disposal of anatomical waste.
Let's Talk!
Your time is valuable, and we don’t want to play hard to get. You can either phone us directly on the details listed on our contact page, or feel free to fill out this short form and one of our team members will get back to you as quickly as possible.
